16 Sep
Research on the Application of GLDA-4NA in Cosmetics
1. Introduction
As consumers demand greater safety and environmental friendliness in cosmetics, the use of traditional preservatives and chelating agents (such as EDTA) is increasingly restricted due to potential irritation and environmental accumulation. GLDA-4NA (tetrasodium L-glutamic acid diacetate), a novel bio-based chelating agent, has gained widespread application in cosmetics due to its excellent biodegradability, mildness, and versatility. This article reviews the chemical properties, mechanism of action in cosmetics, specific applications, and related research progress of GLDA-4NA, citing relevant literature to support its safety and efficacy.

2. Chemical Properties of GLDA-4NA
GLDA-4NA is a green chelating agent based on L-glutamic acid with the chemical formula C9H9NNa4O8. Its molecular structure contains two carboxylic acid groups and one amino group, resulting in the following characteristics:
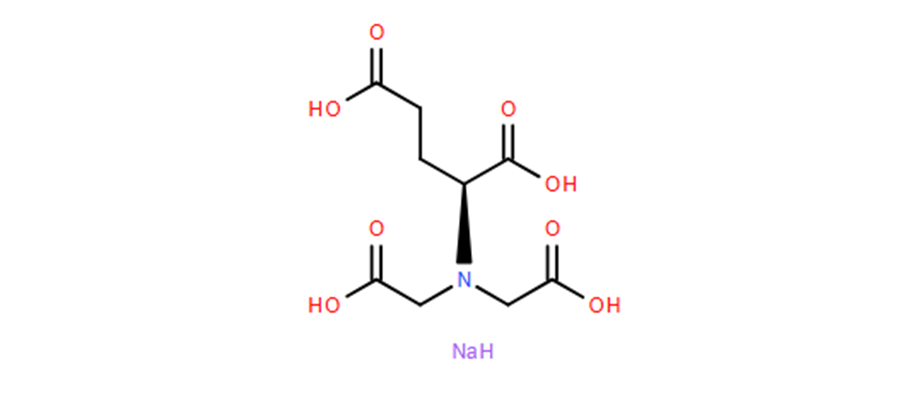
High Chelating Ability: Its chelating ability for metal ions such as Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, and Fe²⁺/Fe³⁺ is similar to that of EDTA (log K ≈ 10.5 for Ca²⁺), but it is more easily degradable.
Excellent Biodegradability: In the OECD 301B test, the degradation rate is >90% within 28 days, significantly higher than that of EDTA (<5%).
Mild and Low Irritation: It has a wide pH range (3-12) and is extremely low in irritation to skin and mucous membranes.
3. Mechanism of Action of GLDA-4NA in Cosmetics
3.1 Chelating Metal Ions and Stabilizing Formulas
Metal ions (such as Ca²⁺ and Fe³⁺) in cosmetics may catalyze oil oxidation, cause product discoloration, or reduce preservative activity. GLDA-4NA improves product stability by chelating these ions. For example:
In lotions and sunscreens, GLDA-4NA can prevent Fe³⁺-induced vitamin C degradation, extending shelf life.
In shampoo, it can reduce Ca²⁺ deposition in hard water, preventing dry hair.
3.2 Replacing Traditional Preservatives and Enhancing Antimicrobial Effectiveness
Because traditional preservatives (such as MIT and CMIT) can cause skin allergies, GLDA-4NA can serve as a supplementary preservative, inhibiting microbial growth by chelating metal ions. Studies have shown:
- Lotions containing 1% GLDA-4NA exhibit >90% inhibition against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Combining with phenoxyethanol can reduce the dosage of phenoxyethanol and reduce irritation.
3.3 Improving the Mildness of Cleansing Products
In cleansing products such as facial cleansers and body washes, GLDA-4NA can reduce soap scum formation, improve foaming, and reduce the irritation of surfactants such as SLS/SLES.

4. Specific Application Examples
4.1 Anti-Aging Skincare Products
GLDA-4NA stabilizes antioxidant ingredients (such as vitamin E and polyphenols) and prevents metal ion-catalyzed oxidation reactions. One study showed that a serum containing 0.5% GLDA-4NA retained over 85% of its antioxidant activity over 12 weeks, while the control (no chelating agent) retained only 60%.
4.2 Hair Dyes and Perms
In oxidative hair dyes, GLDA-4NA chelates Cu²⁺/Fe²⁺, preventing premature dye degradation and improving color uniformity. It can also reduce hair damage caused by alkaline perms.
4.3 Natural and Organic Cosmetics
Because GLDA-4NA meets ECOCERT and COSMOS organic certification standards, it is widely used in natural skincare products as an EDTA replacement.
5. Safety and Regulatory Status
Skin Irritation Testing: According to ECHA (2020), GLDA-4NA did not cause skin or eye irritation at a 5% concentration (rabbit model).
Regulatory Approval: It is included in the list of permitted ingredients under the EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC No. 1223/2009) and the China Cosmetics Safety Technical Specifications (2021 edition).
6. Challenges and Future Trends
Despite its significant advantages, GLDA-4NA remains more expensive than traditional chelating agents (such as EDTA). Future research directions include:
1. Optimizing compounding technology (e.g., combining with natural preservatives);
2. Expanding its application in color cosmetics (e.g., foundation and mascara) to prevent discoloration caused by metal ions.
7. Conclusion
Due to its efficient chelation, biodegradability, and mild properties, GLDA-4NA is an ideal alternative to EDTA in the cosmetics industry. With the increasing adoption of green chemistry and sustainable development concepts, its application in skincare, cleansing, and hair dye products is expected to expand.






