16 Sep
Research on the Application of MGDA-3NA in Water Treatment
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of industrialization and urbanization, water pollution has become increasingly serious, particularly the harm caused by heavy metal ions, calcium and magnesium scaling, and organic pollutants to water bodies. Traditional water treatment methods such as chemical precipitation, ion exchange, and membrane separation suffer from low efficiency, high costs, and secondary pollution. Against this backdrop, environmentally friendly chelating agents, due to their high efficiency and biodegradability, have become a research hotspot. MGDA-3NA (methylglycine diacetic acid trisodium salt), as a new green chelating agent, exhibits broad application prospects in water treatment due to its excellent metal ion complexing ability, biodegradability, and environmental friendliness.

2. Chemical Properties of MGDA-3NA
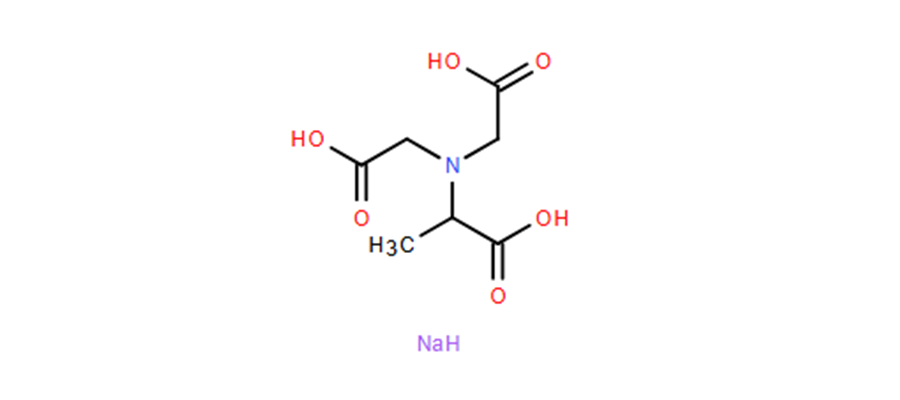
MGDA-3NA is an aminocarboxylic acid chelating agent with the chemical formula **C7H8NNa3O6**. Its molecular structure contains three carboxylic acid groups and one amino group, capable of forming stable, water-soluble complexes with metal ions through multidentate coordination. Its features include:
High chelating capacity: Its complexation constant for metal ions such as Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, Fe³⁺, Cu²⁺, and Pb²⁺ is significantly higher than that of traditional chelating agents such as EDTA and NTA.
Biodegradability: In the OECD 301B standard test, it biodegrades over 80% within 28 days, significantly higher than EDTA (which is virtually non-degradable).
High temperature resistance and wide pH adaptability: It remains stable within the pH range of 2-12, making it suitable for treating acidic or alkaline wastewater.
3. Main Applications of MGDA-3NA in Water Treatment
3.1 Heavy Metal Removal from Industrial Wastewater
Heavy metal contamination is a major problem in wastewater from industries such as electroplating, mining, and battery manufacturing. MGDA-3NA can convert free heavy metal ions (such as Cd²⁺, Hg²⁺, and Ni²⁺) into soluble complexes through chelation, which can then be removed through precipitation or membrane separation. For example:
Electroplating wastewater treatment: Adding MGDA-3NA (0.5-2 g/L) can achieve a copper ion removal rate of over 95% and reduce sludge volume by 30%.
Comparative Advantages: Compared to EDTA, MGDA-3NA is more efficient at low dosages, and residuals can be subsequently degraded through biological treatment, preventing long-term environmental accumulation.
3.2 Scale and Corrosion Inhibition
In circulating cooling water and boiler water systems, calcium and magnesium ions easily form carbonate or sulfate scale. MGDA-3NA achieves dynamic scale inhibition by chelating Ca²⁺/Mg²⁺ and preventing crystal nucleation growth:
Experimental Data: At 80°C and a Ca²⁺ concentration of 500 mg/L, 10 mg/L of MGDA-3NA reduced scaling by 90%.
Synergistic Effect: Combining with polyacrylic acid (PAA) further enhances scale inhibition and extends equipment life.
3.3 Detergent and Printing and Dyeing Wastewater Treatment
Traditional phosphorus-containing detergents can easily lead to eutrophication of water bodies. MGDA-3NA, as a phosphorus-free chelating agent, can replace STPP (sodium tripolyphosphate):
Decolorization of Printing and Dyeing Wastewater: The complex formed by MGDA-3NA and Fe²⁺ catalyzes H₂O₂ to produce hydroxyl radicals, degrading azo dyes (such as Reactive Black 5) with a decolorization efficiency exceeding 85%.
Low Biological Toxicity: Its degradation products are significantly less toxic to aquatic microorganisms than NTA.
3.4 Soil Remediation and Radioactive Wastewater Treatment
Soil Leaching: MGDA-3NA solutions can extract Cd and Pb from contaminated soils, with an extraction efficiency 20%-40% higher than that of citric acid.
Nuclear Waste Treatment: MGDA-3NA has a strong chelating ability for radioactive metals such as uranium (UO₂²⁺) and plutonium (Pu⁴⁺), reducing their migration into the environment.

4. Environmental and Economic Benefit Analysis
Environmental Benefits: MGDA-3NA has an LD50 (oral dose in rats) of >2000 mg/kg, making it a low-toxic substance. Its degradation products are CO2 and water.
Cost Comparison: Although its unit price is slightly higher than that of EDTA, its usage is reduced by 30%-50%, resulting in lower overall treatment costs.
5. Challenges and Prospects
Currently, the promotion of MGDA-3NA is limited by:
1. High concentrations may interfere with subsequent biochemical treatment;
2. Inadequate chelation efficiency for certain rare earth metals (such as La⁺).
Future research directions include modification to enhance selectivity, development of complex formulations, and optimization of process parameters.
6. Conclusion
MGDA-3NA has become a key chemical in the water treatment industry due to its high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and multifunctionality. With tightening environmental regulations and the development of green chemistry, its application in heavy metal wastewater remediation, circulating water systems, and soil remediation will further expand, providing key technical support for sustainable development.






